Difference between revisions of "OCC"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+Presentation Slides link from OpenPOWER Development Congress San Francisco 2017) |
(add helpful diagram) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|name=On-Chip Controller | |name=On-Chip Controller | ||
|abbr=OCC | |abbr=OCC | ||
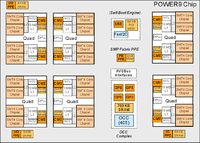
| − | |desc=Auxillary Power ISA microprocessor on [[OpenPOWER]] CPUs. Periodically monitors chip workload, power consumption and temperature readings. Transmits temperature readings to the BMC to allow it to set appropriate fan speeds. The OCC implements any applicable power caps and supports programmable TDP limits.}} | + | |desc=[[File:P9_ppe_instances.png|200px|thumb|right|OCC on [[POWER9]]]] Auxillary Power ISA microprocessor on [[OpenPOWER]] CPUs. Periodically monitors chip workload, power consumption and temperature readings. Transmits temperature readings to the BMC to allow it to set appropriate fan speeds. The OCC implements any applicable power caps and supports programmable TDP limits.}} |
OCC firmware is loaded at boot as part of the boot process and is open source. | OCC firmware is loaded at boot as part of the boot process and is open source. | ||
Latest revision as of 03:19, 22 February 2018

OCC on POWER9
Auxillary Power ISA microprocessor on OpenPOWER CPUs. Periodically monitors chip workload, power consumption and temperature readings. Transmits temperature readings to the BMC to allow it to set appropriate fan speeds. The OCC implements any applicable power caps and supports programmable TDP limits.
OCC firmware is loaded at boot as part of the boot process and is open source.
The CME, SGPE and PGPE auxillary microprocessors handle various power management responsibilities and are managed by the OCC.