Difference between revisions of "OpenPOWER Firmware"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Components: linking both mentions of SEEPROM in Loaded from column, since sort order is unknown) |
(→Components: continuing previous edits; moving source links to firmware column,) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
! Function | ! Function | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | SBE - OTPROM |
| − | |||
| − | |||
[https://git.raptorcs.com/git/talos-sbe/tree/src/boot/otprom_init.S Source] | [https://git.raptorcs.com/git/talos-sbe/tree/src/boot/otprom_init.S Source] | ||
| − | | | + | | [[Self-Boot Engine|SBE]] core (on CPU) |
| + | | [[OTPROM|OTPROM]] (on CPU die) | ||
| + | | The portion of [[Self-Boot Engine|Self-Boot Engine]] (SBE) firmware permanently written via eFuses into the POWER9 silicon's OTPROM | ||
* very first instructions executed | * very first instructions executed | ||
| − | * loads SBE firmware from SEEPROM into SBE core | + | * loads remaining SBE firmware from SEEPROM into SBE core |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | SBE - SEEPROM |
| − | |||
| − | |||
[https://git.raptorcs.com/git/talos-sbe/tree/ Source] | [https://git.raptorcs.com/git/talos-sbe/tree/ Source] | ||
| − | | | + | | [[Self-Boot Engine|SBE]] core (on CPU) |
| + | | SBE [[SEEPROM|SEEPROM]] (on CPU) | ||
| + | | The portion of [[Self-Boot Engine|Self-Boot Engine]] (SBE) firmware run from rewritable [[SEEPROM|SEEPROM]] | ||
* initialises CPU core | * initialises CPU core | ||
* loads Hostboot Bootloader | * loads Hostboot Bootloader | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Hostboot Bootloader (HBBL) | | Hostboot Bootloader (HBBL) | ||
| + | [https://git.raptorcs.com/git/talos-hostboot/tree/src/bootloader Source] | ||
| CPU core | | CPU core | ||
| − | | SBE [[SEEPROM|SEEPROM]] (on CPU | + | | SBE [[SEEPROM|SEEPROM]] (on CPU) |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
* first code which runs on main CPU cores; loads and executes rest of Hostboot | * first code which runs on main CPU cores; loads and executes rest of Hostboot | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Hostboot|Hostboot]] | | [[Hostboot|Hostboot]] | ||
| + | [https://git.raptorcs.com/git/talos-hostboot/tree/ Source] | ||
| CPU core | | CPU core | ||
| [[PNOR|PNOR]] (SPI Flash) | | [[PNOR|PNOR]] (SPI Flash) | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
* initialises DRAM (memory training, zeroing of ECC memory, etc.), processor bus, memory buffers | * initialises DRAM (memory training, zeroing of ECC memory, etc.), processor bus, memory buffers | ||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Skiboot|Skiboot]] | | [[Skiboot|Skiboot]] | ||
| + | [https://git.raptorcs.com/git/talos-skiboot/tree/ Source] | ||
| CPU core | | CPU core | ||
| [[PNOR|PNOR]] (SPI Flash) | | [[PNOR|PNOR]] (SPI Flash) | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
* initialises PCIe controllers, device trees, real time clock, NVlink, sensors | * initialises PCIe controllers, device trees, real time clock, NVlink, sensors | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Skiroot]]/[[Petitboot|Petitboot]] | | [[Skiroot]]/[[Petitboot|Petitboot]] | ||
| + | [https://git.raptorcs.com/git/talos-petitboot/ Source] | ||
| CPU core | | CPU core | ||
| [[PNOR|PNOR]] (SPI Flash) | | [[PNOR|PNOR]] (SPI Flash) | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
* [[Skiroot]] refers to the Linux kernel and initramfs which runs from RAM | * [[Skiroot]] refers to the Linux kernel and initramfs which runs from RAM | ||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| OCC firmware | | OCC firmware | ||
| − | | [[On-Chip Controller|OCC]] core (on CPU | + | [https://git.raptorcs.com/git/talos-occ/tree/ Source] |
| + | | [[On-Chip Controller|OCC]] core (on CPU) | ||
| [[PNOR|PNOR]] (SPI Flash) | | [[PNOR|PNOR]] (SPI Flash) | ||
| − | |||
| The [[On-Chip Controller|On-Chip Controller]] (OCC) manages: | | The [[On-Chip Controller|On-Chip Controller]] (OCC) manages: | ||
* thermal regulation of CPU chip, turbo frequency selection, voltage ID selection, power measurement, etc. | * thermal regulation of CPU chip, turbo frequency selection, voltage ID selection, power measurement, etc. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| CME [[HCODE]] | | CME [[HCODE]] | ||
| − | | [[CME]] cores (on CPU | + | [https://git.raptorcs.com/git/talos-hcode/tree/ Source] |
| + | | [[CME]] cores (on CPU) | ||
| [[PNOR|PNOR]] (SPI Flash) | | [[PNOR|PNOR]] (SPI Flash) | ||
| − | |||
| The [[Core Management Engine|Core Management Engines]] (CME) are auxillary cores used for power management purposes. They are ultimately responsible to the OCC. | | The [[Core Management Engine|Core Management Engines]] (CME) are auxillary cores used for power management purposes. They are ultimately responsible to the OCC. | ||
* There is one CME for every pair of SMT4 cores. | * There is one CME for every pair of SMT4 cores. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| SGPE and PGPE [[HCODE]] | | SGPE and PGPE [[HCODE]] | ||
| − | | [[SGPE]] and [[PGPE]] cores (on CPU | + | [https://git.raptorcs.com/git/talos-hcode/tree/ Source] |
| + | | [[SGPE]] and [[PGPE]] cores (on CPU) | ||
| [[PNOR|PNOR]] (SPI Flash) | | [[PNOR|PNOR]] (SPI Flash) | ||
| − | |||
| [[GPE|General Purpose Engine]] (GPE) cores which assist, and are managed by, the OCC. | | [[GPE|General Purpose Engine]] (GPE) cores which assist, and are managed by, the OCC. | ||
* The [[SGPE|Stop GPEs]] (SGPEs) are part of the mechanism for resuming execution after a STOP instruction is executed (which is a Power ISA instruction which halts the processor). | * The [[SGPE|Stop GPEs]] (SGPEs) are part of the mechanism for resuming execution after a STOP instruction is executed (which is a Power ISA instruction which halts the processor). | ||
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| IOPPE [[HCODE]] | | IOPPE [[HCODE]] | ||
| − | | [[IOPPE]] cores (on CPU | + | [https://git.raptorcs.com/git/talos-hcode/tree/ Source] |
| + | | [[IOPPE]] cores (on CPU) | ||
| [[PNOR|PNOR]] (SPI Flash) | | [[PNOR|PNOR]] (SPI Flash) | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
* Involved in CAPI support. | * Involved in CAPI support. | ||
|- style="background-color:#e0e0e0;" | |- style="background-color:#e0e0e0;" | ||
| [[OpenBMC]] | | [[OpenBMC]] | ||
| + | [https://git.raptorcs.com/git/talos-openbmc/tree/ Source] | ||
| BMC chip | | BMC chip | ||
| BMC SPI Flash | | BMC SPI Flash | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
<small>(This is not part of OpenPOWER firmware, but is mentioned to give a picture of the division of responsibilities. Not all POWER9 systems use a BMC; IBM systems use a [[FSP]].)</small> | <small>(This is not part of OpenPOWER firmware, but is mentioned to give a picture of the division of responsibilities. Not all POWER9 systems use a BMC; IBM systems use a [[FSP]].)</small> | ||
Revision as of 11:12, 30 June 2021
OpenPOWER Firmware is an open-source alternative to OpenFirmware and proprietary IBM firmware used on Power machines.[1] It is a general name for many separate pieces of software used to start recent Power Architecture chips made by IBM.[2]
OpenBMC is a separate project that creates firmware for the Baseboard Management Controller.
Components
| Firmware | Executed on | Loaded from | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| SBE - OTPROM | SBE core (on CPU) | OTPROM (on CPU die) | The portion of Self-Boot Engine (SBE) firmware permanently written via eFuses into the POWER9 silicon's OTPROM
|
| SBE - SEEPROM | SBE core (on CPU) | SBE SEEPROM (on CPU) | The portion of Self-Boot Engine (SBE) firmware run from rewritable SEEPROM
|
| Hostboot Bootloader (HBBL) | CPU core | SBE SEEPROM (on CPU) |
|
| Hostboot | CPU core | PNOR (SPI Flash) |
|
| Skiboot | CPU core | PNOR (SPI Flash) |
|
| Skiroot/Petitboot | CPU core | PNOR (SPI Flash) | |
| OCC firmware | OCC core (on CPU) | PNOR (SPI Flash) | The On-Chip Controller (OCC) manages:
|
| CME HCODE | CME cores (on CPU) | PNOR (SPI Flash) | The Core Management Engines (CME) are auxillary cores used for power management purposes. They are ultimately responsible to the OCC.
|
| SGPE and PGPE HCODE | SGPE and PGPE cores (on CPU) | PNOR (SPI Flash) | General Purpose Engine (GPE) cores which assist, and are managed by, the OCC.
|
| IOPPE HCODE | IOPPE cores (on CPU) | PNOR (SPI Flash) |
|
| OpenBMC | BMC chip | BMC SPI Flash |
(This is not part of OpenPOWER firmware, but is mentioned to give a picture of the division of responsibilities. Not all POWER9 systems use a BMC; IBM systems use a FSP.)
|

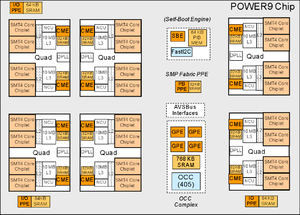
Diagram of main and auxillary cores on POWER9
Process
- SBE executes OTPROM, which loads SEEPROM firmware into SBE PIBMEM
- SBE executes SEEPROM firmware
- OpenBMC uses FSI interface to start SBE
- SBE loads Hostboot
- Hostboot loads Skiboot
- Skiboot loads OCC, Skiroot
- Petitboot application within Skiroot loads the operating system
- OS talks to firmware through OPAL
References
- ↑ Kerr, Jeremy. OpenPOWER: building an open-source software stack from bare metal. LCA 2015 - video on YouTube
- ↑ Smith, Stewart. Adventures in OpenPOWER Firmware. LCA 2016 - video on YouTube
See also
External Links
- OpenPOWER firmware source code on GitHub
- For a better understanding of OpenPOWER firmware and boot processes, see:
- Bug tracker for firmware issues specific to Raptor CS products: https://bugs.raptorengineering.com/